Decision Making Statements
- It is the type of control flow statements which will check the given condition before performing a perticular task.
- It is classified into
1) if (simple if) 2) if else 3) else if ladder 4) nested if 5) switch
1) if (simple if)
- It is the type of decision making statement.
- It is a keyword in java.
- It will check the given condition first, if the condition is true then only it will execute the statements which are present in the if block.
- Syntax
if (condition) statement1;if (condition) { statement1; statement2; } -
Flowchart
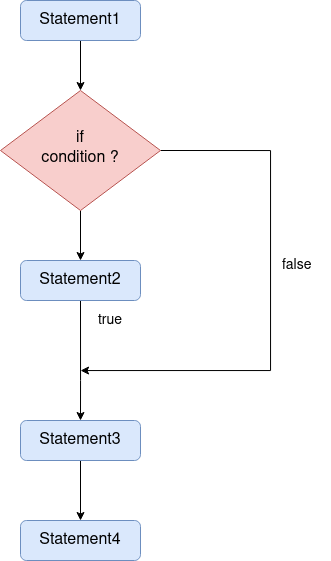
- e.g.
class Program1 { public static void main (String[]args) { System.out.println("Hi"); if (true) System.out.println("Hello"); System.out.println("My name is Sunil"); } } - Ans = Hi, Hello, My name is Sunil
class Program2
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
System.out.println("Hi");
if (false)
System.out.println("Hello");
System.out.println("My name is Sunil");
}
}
- Ans = Hi, My name is Sunil
class Program3
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
System.out.println("Hi");
if (true)
{
System.out.println("Hello");
System.out.println("Please Reply...");
}
System.out.println("Block")
}
}
- Ans = Hi, Hello, Please Reply..
class Program3
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
System.out.println("Hi");
if (true)
{
System.out.println("Hello");
System.out.println("Please Reply...");
}
System.out.println("Block")
}
}
- Ans = Hi, Hello, Please Reply.., Block
class Program4
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
System.out.println("Hi");
if (false)
{
System.out.println("Hello");
System.out.println("Please Reply...");
}
System.out.println("Block")
}
}
- Ans = Hi, Block
2) if else
- It is the type of decision making statement.
- It will check the given condition first, if the condition is true then only it will execute the statements which are present in the if block and if the condition is false that time it will execute the statements present inside else block.
- Syntax
if (condition) statement; else statement;if (condition) { statement1; statement2; } else { statement3; statement4; } -
Flowchart
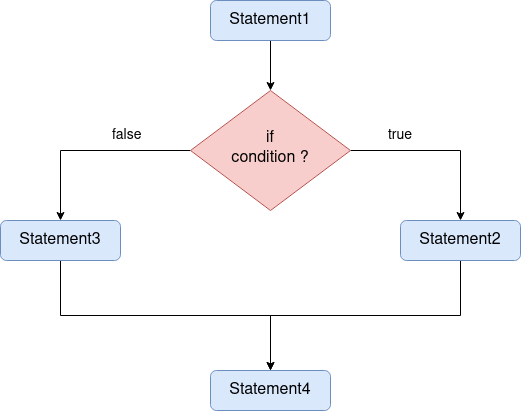
- e.g.
class Program1 { public static void main (String[]args) { System.out.println("Hi"); if (true) System.out.println("Hello"); else System.out.println("By"); } } -
Ans = Hi, Hello
- e.g.
class Program2 { public static void main (String[]args) { System.out.println("Goa Plan"); if (false) { System.out.println("Ask Money"); System.out.println("Enjoy Goa"); System.out.println("Come Back Home"); } else { System.out.println("Plan Fails"); System.out.println("No Money"); System.out.println("Sit in Home"); } } } -
Ans = Goa Plan, Plan Fails, No Money, Sit in Home
- Que. Write a program to check whether the given number is divisible by 3 & 7. If it is divisible then display pass else fail.
- Number = 21
class Que1
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
int num = 21;
if (num % 3 == 0 && num % 7 == 0)
{
System.out.println("Pass");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Fail");
}
}
}
-
Ans = Pass
- Que. Write a program to check whether the given number even or odd.
- Number = 20
class Que2
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
int num = 20;
if (num % 2 == 0)
{
System.out.println("Given number is even number");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Given number is odd number");
}
}
}
- Ans = Given number is even number
3) else if ladder / if-else-if
- Whenever we have to execute group of statements which will have multiple conditions that time we have to use else if ladder/if-else-if statements.
- Syntax
if (condition)
{
statement1;
}
else if (condition)
{
statement2;
}
else if (condition)
{
statement3;
}
else
{
statement4;
}
-
Flowchart
- Que. Write a program to check whether the given number is
i) If number is even print “Hi”
ii) If number is divisible by 3 & 5 print “By”
iii) If number is odd & divisible by 7 print “By By”
iv) else “Good By” - number = 20.
class Que1
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
int n = 20;
if (n % 2 == 0)
{
System.out.println("Hi");
}
else if (n % 2 == 0 && n % 5 == 0)
{
System.out.println("By");
}
else if (n % 2 != 0 && n % 7 == 0 )
{
System.out.println("By By");
}
else
{
System.out.println("Good By");
}
}
}
- Ans = Hi
4) Nested if
- An if condition inside an another if is called as nested if.
- If all given condition is true then only statement1 is executed otherwise statement2 in else block will get executed.
- Syntax
if (condition1)
{
if (condition2)
{
if (condition3)
{
statement1;
}
}
}
else
{
statement 2;
}
- Flowchart
class Eg1
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
int n = 10;
if (n % 2 == 0)
{
System.out.println("Step 1");
n = 10 * 2;
if(n == 20 )
{
System.out.println("Step 2");
n = 20 + 20;
if ( n == 40)
{
System.out.println("Step 3");
System.out.println("All True");
}
}
}
else
{
System.out.println("All False");
}
}
}
- Ans = Step 1, Step 2, Step 3, All True
5) Switch
- It is a special decision making statement in java.
- switch is a keyword in java.
- Inside a switch we can pass either expression/literal, other than boolean condition.
- The result of the expression is compared with the values of each case.
- If there is a match, the associated block of code is executed.
- The break and default keywords are optional.
- Syntax
switch (expression/literal)
{
case option 1 :
{
statement1;
break;
}
case option 2 :
{
statement1;
break;
}
default :
{
statements;
}
}
- Note
- For each case we have to provide the break keyword, otherwise it will execute all statements present below the given statement.
- break is keyword in java.
- It will help to transfer the control out of the block.
- Que. Write a program to check whether the given number is even/odd using switch.
- number = 60
class Que1
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
int a = 60;
switch (a % 2)
case 0 :
{
System.out.println("even");
break;
}
case 1 :
{
System.out.println("odd");
break;
}
}
}
-
Ans = even
- Que. Write a program to check whether the given character is vowel or not.
- number = 60
class Que2
{
public static void main (String[]args)
{
char ch = 'i';
switch (ch)
case 'a' :
System.out.println("vowel");
break;
case 'e' :
System.out.println("vowel");
break;
case 'i' :
System.out.println("vowel");
break;
case 'o' :
System.out.println("vowel");
break;
case 'u' :
System.out.println("vowel");
break;
default :
System.out.println("consonant");
}
}
- Ans = even