Looping Statements
- It is the type of the control flow statement which will execute the group of statements multiple times by checking the condition in each time.
- Looping statement is classified into 1) for loop 2) while loop 3) do while loop
1) for loop
- It is the type of looping statements which will have fix initial and final point to execute the given statements multiple times.
-
Syntax
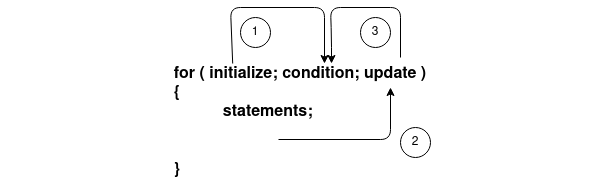
- Que1 Print “*” four times.
class Que1
{
public static void main(String[]args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
System.out.println("*");
}
}
}
- Ans =
*
*
*
*
* - Que2 Write the program to print even number between 100 to 80 using for loop.
class Que2
{
public static void main(String[]args)
{
for (int i = 100; i >= 80; i--)
{
if (i % 2 == 0)
{
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
}
-
Ans =
100
98
96
94
92
90
88
86
84
82
80 -
Que3 Write the program to find summation of first ten numbers starting from 1.
class Que3
{
public static void main(String[]args)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
sum = sum + i;
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
-
Ans = 55
-
Que4 Write the program to find summation of all even numbers between 20 to 10 using for loop.
class Que4
{
public static void main(String[]args)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 20; i >= 10; i--)
{
if(i % 2 == 0 )
{
sum = sum + i;
}
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
- Ans = 90
2) while loop
- It will execute the group of statements multiple times until condition is true.
- while loop first check the condition if it is true then it will execute the statements.
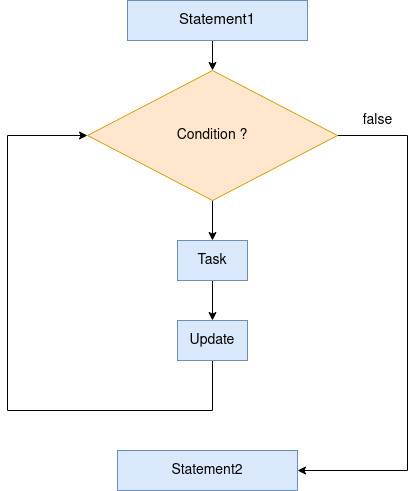
- Syntax
while (condition) { statements; update; } -
flowchart
- eg.
class Program 1
{
public static void main (String [] args)
{
while (false)
{
System.out.println("Hello World")
}
}
}
- Ans = Unreachable Statement (Compile Time Error)
class Program2
{
public static void main (String [] args)
{
int i =0;
while (i < 5)
{
System.out.println("*")
}
}
}
-
Ans =
*
*
*
*
* -
Que1 Write a program to print the numbers in reverse order from 20 to 10 using while loop
class Que1
{
public static void main(String[]args)
{
int i = 20;
while (i >= 10)
{
System.out.print(i +" ");
i--;
}
}
}
-
Ans = 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10
-
Que2 Write a program to print all the even numbers between 25 to 50 using while loop
class Que2
{
public static void main(String[]args)
{
int i = 25;
while (i <= 50)
{
if (i % 2 == 0)
System.out.print(i +" ");
i++;
}
}
}
-
Ans = 26 28 30 32 34 36 38 40 42 44 46 48 50
-
Que3 Write a program to print all the numbers which are divisible by 3 & 7 between 100 to 50
class Que3
{
public static void main(String[]args)
{
int i = 100;
while (i >= 50)
{
if (i % 3 == 0 && i % 7 == 0)
System.out.print(i +" ");
i--;
}
}
}
- Ans = 84 63
- Note
Increment/decrement always gives after completing decision making block.
3) do while loop
- It is used to execute group of statements multiple times depending on condition.
- do while loop executes atlest once even though condition is false.
-
do will first executes statements and then check the condition.
- Syntax
do
{
statements;
update;
}
while(condition);
- Note
In do while loop the while condition should be ended with semicolon (;).
In do while even if condition either true/false, the statement gets execute atlest onces. - eg.1
class Example1
{
public static void main(String[]args)
{
int a = 0;
do
{
System.out.print(a++);
}
while (a > 10);
}
}
- Ans = 0
- Que1 Write a program to print all the numbers between 0 to 10 using do while loop.
class Que1
{
public static void main(String[]args)
{
int a = 0;
do
{
System.out.print(a +" ");
a++;
}
while (a <= 10);
}
}
-
Ans = 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
-
Que2 Write the difference between whie loop and do while loop.
| No | while loop | do while loop |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Condition is tested at the beginning of the loop. | Condition is tested at the end of the loop. |
| 2. | If condition is true then only statements will executed. | Even condition is true/false statements will executed at least once. |
| 3. | In while loop condition should not be ended with (;) semicolon. | In do while loop condition should be ended with (;) semicolon. |